| Citation: Hou Shi-Tian, Cai Jing-Yi, Tan Ke-Yan, Yang Hong, Hu Xin, Wang Zhe, Yuan Xin. 2019. A mine drainage treatment system for AMD in remediation of metal sulfide mines. China Geology, 2(3), 396‒397. doi: 10.31035/cg2018112. |
In the process of mining, sorting and smelting metal sulfide mines, a large amount of acid mine drainage (AMD) containing concentrated sulfate (SO42−) and various metal elements (Fe, Mn, Cu, Zn, Ni, etc.) are produced. In order to solve current problems of mine acid drainage, we have improved the existing repair technology based on bio-geochemical technology, and provided a new treatment system for AMD from metal sulfide mines.
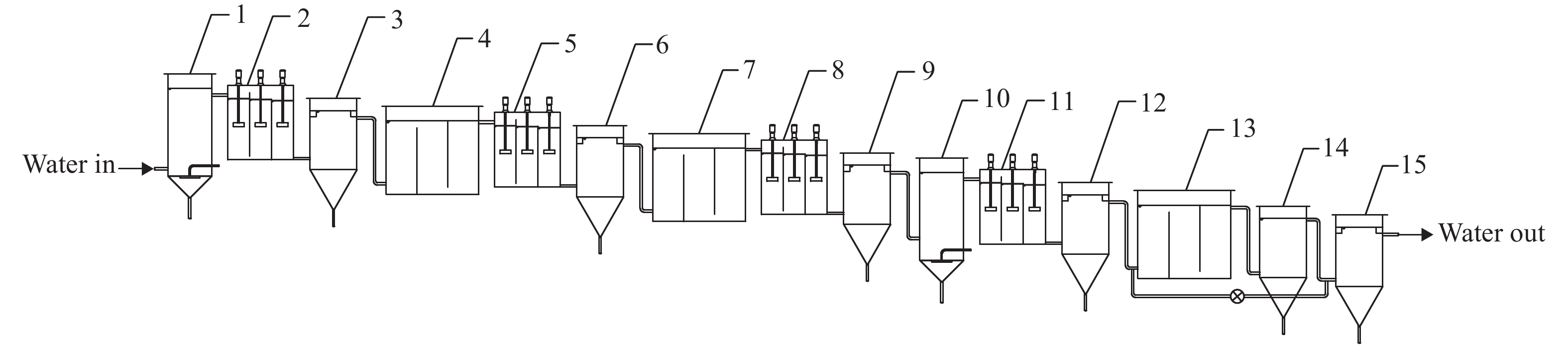
As shown in Fig. 1 and Fig. 2, an AMD treatment system is mainly composed of 5 units. They are the iron removal unit (1, 2, 3), sulfate reduction unit (4, 5,6), sulfur recovery unit(7, 8, 9), manganese removal unit (10, 11, 12) and end purification unit(13, 14, 15) successively. In order to achieve a good separation and recovery effect, each unit is equipped with a reaction tank, flocculation tank and sedimentation tank. All equipment is distributed from left to right, and the height difference is used to ensure the order of the water in and out of each process.
When AMD flowed through this system, firstly, in the iron precipitation unit, Fe2+ was oxidized to Fe3+ by aeration and hydrogen peroxide oxidation, and after adjusting the pH value of the drainage, Fe3+ in the solution formed a precipitate of Fe(OH)3, which is removed by flocculation and precipitation separation.
In the next procedure, the release of sulfate-reducing bacteria (SRB) in the sulfate oxidation tank reduced SO42− to S2− in wastewater producing CuS with Cu2+, which reached an object to remove Cu2+ and some SO42− in water by flocculation and precipitation.
After that, adding sulfur oxidizing bacteria (SOB) in the sulfur oxidation tank, oxidizing S2− to elemental S in the sulfur oxidation tank by aeration and bacteria action, and produced S was removed from the water by flocculation precipitation.
Then, aerobic and releasing manganese oxidizing bacteria in the manganese oxidation tank can oxidize Mn2+ in the wastewater to insoluble high-valence manganese, and remove Mn2+ in the wastewater by flocculation and sedimentation.
In the next step, the active sludge was placed in the terminal oxidation tank and aerated, which can oxidize excess organic matter in the wastewater and remove a large amount of COD.
After all, the modified attapulgite was added into the mineral adsorption tank, and its ion exchange adsorption performance can remove other heavy metal elements such as Mn2+, Zn2+ and Ni2+ remained in the wastewater.
The AMD treatment system can effectively remove metal elements such as Fe, Mn, Cu, Zn, Ni and S elements in AMD by utilizing physical-chemical-biological comprehensive treatment technology to ensure the treatment effect of wastewater and didn’t cause secondary pollution; In addition, this system can realize the recycling of various metal elements and sulfur elements by collecting and treating the sediments in each sedimentation tank.
As shown in Table 1, Fe, Cu2+, Mn2+ and SO42− in AMD of Dexing Copper Mine were removed by 99%, 99%, 99% and 33% in this treatment system. Simultaneously, the Fe and Cu were recovered. The pH of the effluent was adjusted from 2.70 to about 8.60, and the effluent water quality reach the first level standard of National Integrated Wastewater Discharge Standard (GB8978-1996).
| Chemical composition | pH | Fe/(mg/L) | Cu2+ | Mn2+ | SO42−/ (mg/L) |
| Before | 2.70 | 226 | 24 | 27 | 7200 |
| After | 8.60 | 0.031 | 0.025 | 0.059 | 4800 |
We have developed a whole system based on the technology of bio-geochemistry, the AMD treating system combines with various drainage remediation methods, which has the advantages of concise structure, low cost, easy operation, high processing efficiency, excellent purification effect and lower energy consumption. Based on the system, not only the treatment results of the AMD can be enhanced, but also the secondary pollution can be avoided. The AMD treatment technology is economically feasible and can be used as a technical model for repairing AMD in metal sulfide mines, and provides a reference for other types of mine pollution remediation.
This technology has been granted a national patent for invention(ZL 201811502722.0) (Fig. 3). This study was jointly funded by China Geological Survey Basic Research Business Expenses Project (YYWF201722) and China Geological Survey Project (DD20190655). Thanks to the contribution and assistance of Key Laboratory of Beijing for Water Quality Science and Water Environmental Recovery Engineering, Beijing University of Technology, and Jiangxi Dexing Copper Mine Baitai Company.
| Chemical composition | pH | Fe/(mg/L) | Cu2+ | Mn2+ | SO42−/ (mg/L) |
| Before | 2.70 | 226 | 24 | 27 | 7200 |
| After | 8.60 | 0.031 | 0.025 | 0.059 | 4800 |